Hawaii, known for its stunning natural beauty and diverse cultural heritage, has a significant population of Asians. The presence of Asians in Hawaii is notable and raises curiosity about the reasons behind their concentration in the islands. Exploring the factors that have contributed to this demographic phenomenon provides insights into the historical, cultural, economic, and geographic influences that have shaped Hawaii's Asian community.
Understanding the Asian population in Hawaii is crucial for appreciating the rich cultural tapestry of the islands. Hawaii serves as a unique case study for examining the dynamics of Asian migration, assimilation, and contribution to a society that is geographically distant from Asia. Additionally, recognizing the factors that have attracted Asians to Hawaii can shed light on the larger patterns of Asian migration and diaspora around the world.
This article aims to delve into the historical context, cultural and social influences, economic factors, geographic proximity, and educational/workforce dynamics to understand why there is a substantial Asian population in Hawaii. By examining these factors, we can gain a comprehensive perspective on the reasons behind the prevalence of Asians in Hawaii and appreciate the unique cultural diversity they bring to the islands.
Historical Context
Hawaii's Asian population has deep historical roots that trace back to the early migration patterns of Asians to the islands. Understanding this historical context is essential to comprehend the significant Asian presence in Hawaii today.
In the 19th century, Hawaii experienced an influx of Asian immigrants, primarily driven by the need for labor. Chinese migration played a significant role during this period, with many Chinese workers arriving in Hawaii to work on sugar plantations. They brought with them their unique cultural traditions and skills, contributing to the diverse fabric of Hawaii's society.
The introduction of the Japanese population in Hawaii also played a pivotal role in shaping the Asian community. As the sugar industry grew, Japanese immigrants arrived in substantial numbers to work on the plantations. Their labor and perseverance helped establish Hawaii's reputation as a leading producer of sugar. The influence of the Japanese on agriculture and fishing industries further solidified their presence and contributions in Hawaii.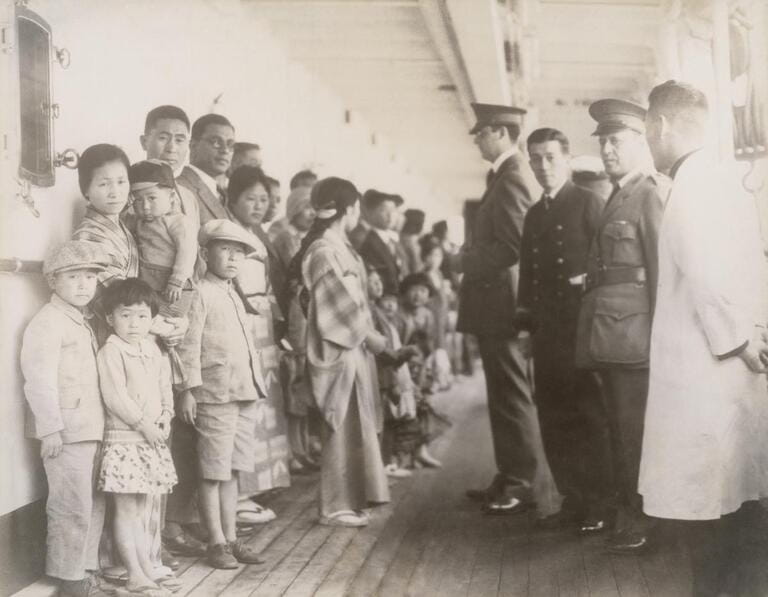
However, Asian migration to Hawaii was not without its challenges. Immigration restrictions and discriminatory laws hindered the entry of Asian immigrants during certain periods. The Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and subsequent legislation significantly reduced Chinese migration to Hawaii. Similarly, the Gentlemen's Agreement of 1907 between the United States and Japan restricted Japanese immigration. These restrictions had a profound impact on Asian migration patterns to Hawaii.
Despite the challenges, the Asian population in Hawaii continued to grow and make substantial contributions to the islands' economy. Chinese immigrants played a pivotal role in trade and commerce, establishing successful businesses and contributing to Hawaii's economic growth. Their entrepreneurial spirit and business acumen helped shape the local economy.
Japanese immigrants, in addition to their contributions in the sugar industry, brought their agricultural expertise to Hawaii. They introduced innovative farming techniques and played a vital role in developing Hawaii's agricultural sector. Japanese influence can still be seen today in the cultivation of rice, fruits, and vegetables in the islands.
Filipino immigrants also made significant contributions to Hawaii's labor force. They filled various roles in the plantation industry and brought their agricultural knowledge and skills to the islands. The hard work and dedication of Filipino laborers helped sustain Hawaii's agricultural production.
Korean immigrants, while relatively smaller in number compared to other Asian groups, have had a notable impact on Hawaii's small business sector. Korean entrepreneurs established thriving businesses, ranging from restaurants to retail shops, enriching the economic landscape of the islands.
The historical context of Asian migration to Hawaii provides valuable insights into the formation and growth of the Asian population. These early immigrants laid the foundation for a diverse and vibrant community that continues to shape the cultural, social, and economic fabric of Hawaii today. By understanding this historical background, we can appreciate the significant contributions and enduring presence of Asians in the islands.
Cultural and Social Influences
The cultural and social influences brought by Asians have played a crucial role in shaping the unique identity of Hawaii. The preservation and transmission of Asian traditions and customs have contributed to the rich cultural tapestry of the islands.
Asian immigrants, along with subsequent generations, have worked diligently to maintain their cultural heritage in Hawaii. Chinese, Japanese, Filipino, Korean, and other Asian ethnic groups have established community organizations, temples, and cultural centers that serve as hubs for preserving their traditions. These institutions provide a platform for cultural events, language classes, and celebrations, fostering a sense of identity and belonging for Asian residents.
The role of Asian languages in Hawaii cannot be understated. Chinese, Japanese, Tagalog, Korean, and other languages are still spoken in households and community gatherings, ensuring the transmission of ancestral languages across generations. Bilingual education programs and language schools have also contributed to the preservation of Asian languages in Hawaii.
Interethnic relationships and cultural fusion have further enriched the social fabric of Hawaii. Over time, intermarriage and cultural exchange have fostered a unique blend of Asian, Hawaiian, and other cultural influences. This fusion can be observed in various aspects of daily life, including food, music, fashion, and festivals. The vibrant Asian-inspired cuisine, such as sushi, dim sum, and Korean barbecue, has become an integral part of Hawaii's culinary landscape.
Moreover, the diverse cultural backgrounds of Hawaii's Asian population have contributed to a deep sense of multiculturalism and acceptance within the community. The concept of ohana (family) and the spirit of aloha have been embraced by Asians and non-Asians alike, fostering a strong sense of unity and inclusivity in Hawaii.
The Asian community has also made significant contributions to the arts and entertainment scene in Hawaii. Asian dancers, musicians, and performers have showcased their talents through traditional performances, as well as contemporary adaptations that blend Asian and Western influences. These artistic expressions serve as a bridge between different cultures and create opportunities for cross-cultural appreciation.
In summary, the cultural and social influences brought by Asians have played a vital role in shaping Hawaii's identity. The preservation of traditions, the existence of cultural institutions, the interethnic relationships, and the fusion of cultures have fostered a vibrant and diverse community in the islands. The ongoing celebration and appreciation of Asian heritage continue to contribute to the unique cultural tapestry of Hawaii.
Economic Factors
The significant presence of Asians in Hawaii can be attributed, in part, to various economic factors that have contributed to their settlement and growth in the islands. These factors highlight the opportunities and economic contributions made by the Asian community.
Hawaii's thriving economy has attracted people from all over the world, including Asians, in search of new opportunities. The islands' strategic location as a Pacific hub and its robust tourism industry have been key drivers of economic growth. The availability of jobs in sectors such as hospitality, retail, construction, and healthcare has attracted individuals and families from Asian countries to seek employment and establish their lives in Hawaii.
Asians have made significant contributions to Hawaii's entrepreneurial landscape. Many Asian immigrants have successfully established their businesses, ranging from restaurants and retail stores to professional services and technology startups. Their entrepreneurial spirit has not only provided job opportunities for the local community but has also added diversity and innovation to Hawaii's business sector.
The allure of Hawaii as a premier tourist destination has drawn millions of visitors from Asia each year. Asian tourists, particularly from Japan, China, South Korea, and Southeast Asian countries, have played a significant role in driving Hawaii's tourism industry. This steady flow of visitors has created a demand for services, accommodations, and attractions, resulting in job opportunities and economic growth in the tourism sector. The presence of Asian tourists has also fostered cultural exchange and strengthened ties between Hawaii and Asian countries.
The economic factors surrounding the presence of Asians in Hawaii have contributed to the growth and prosperity of both individuals and the broader community. Opportunities for employment and entrepreneurship, coupled with the strong tourism industry, have attracted Asians to the islands, leading to their significant economic impact on Hawaii's economy.
It is important to note that while economic factors have played a substantial role in the concentration of Asians in Hawaii, the Asian community's contributions go beyond the economic realm. Their rich cultural heritage, social influence, and active participation in various aspects of Hawaiian society have made them an integral part of the multicultural fabric of the islands.
Geographic Proximity
The geographic proximity of Hawaii to Asia has been a significant factor contributing to the presence of Asians in the islands. This proximity has facilitated cultural exchange, travel, and historical ties between Hawaii and Asian countries.
Situated in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, Hawaii is geographically positioned as a convenient destination for travelers from Asia. Its tropical climate, pristine beaches, and natural beauty have made it an attractive vacation spot for many Asians seeking a tropical paradise. The relative ease of travel and shorter flight distances compared to other popular destinations have made Hawaii a favored choice for Asian tourists.
The geographical proximity of Hawaii to Asian countries, such as Japan, China, South Korea, and the Philippines, has made travel between these regions more accessible. Direct flights and convenient air routes have facilitated the movement of people between Hawaii and Asia, fostering cultural exchange and creating opportunities for business and personal connections. The shorter travel distances and shared time zones have also contributed to the ease of communication and interaction between Hawaii and Asian nations.
Hawaii's historical and cultural ties with Asian countries have further strengthened the connection between the islands and the Asian population. The early migration of Asians to Hawaii, as discussed in the historical context, established a foundation for cultural exchange and influence. Historical events, such as the influx of Japanese immigrants during the plantation era, have created enduring links between Hawaii and Japan. These connections, rooted in history and culture, continue to shape the relationship between Hawaii and various Asian nations.
The geographic proximity of Hawaii to Asia has not only made it a convenient destination for Asian tourists but has also facilitated the establishment of strong cultural, social, and economic ties between Hawaii and Asian countries. The ease of travel, shared time zones, and historical connections have contributed to the presence of Asians in Hawaii, resulting in a diverse and multicultural community that reflects the interconnectedness of the Pacific region.
Education and Workforce
The Asian population in Hawaii has made significant contributions to the education system and the workforce, shaping various sectors and institutions in the islands.
Asian students have consistently demonstrated high academic achievements in Hawaii's education system. Their strong work ethic, emphasis on education, and parental support have resulted in above-average academic performance. Asian students' achievements have positively influenced the overall academic standards in schools and have set a benchmark for excellence. Their success has motivated and inspired students from diverse backgrounds to strive for educational attainment.
Asians in Hawaii have made substantial contributions to various professional fields. They can be found in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, engineering, finance, technology, and education. Many Asian professionals hold leadership positions and play key roles in both the public and private sectors. Their expertise, skills, and work ethic have contributed to the growth and success of Hawaii's economy.
Hawaii's educational institutions, including universities and colleges, have attracted a significant number of Asian students. These institutions offer diverse academic programs, scholarships, and cultural support systems that appeal to Asian students seeking higher education. The presence of Asian students enriches the learning environment, fostering cross-cultural understanding and creating opportunities for cultural exchange within the educational community.
Asian immigrants and their descendants have embraced the value of education and have actively participated in the workforce, contributing their talents and skills to various professional fields. Their achievements in education and representation in the workforce have had a positive impact on Hawaii's education system and economic development, shaping the future of the islands.
Conclusion
The significant presence of Asians in Hawaii is the result of a complex interplay of historical, cultural, economic, geographic, and educational factors. Understanding these factors helps us appreciate the unique cultural diversity and contributions of Asians to the islands.
Hawaii's historical context reveals the early migration patterns of Asians to the islands, driven by labor needs in the sugar and pineapple industries. Despite challenges such as immigration restrictions, Asian immigrants established themselves in Hawaii and made substantial contributions to the local economy.
Culturally and socially, Asians have preserved their traditions, languages, and customs, creating a vibrant tapestry of multiculturalism in Hawaii. Cultural institutions and interethnic relationships have fostered a fusion of traditions and a sense of unity within the community.
Economically, Hawaii's opportunities and growth have attracted Asians seeking employment, entrepreneurship, and investment. The islands' tourism industry, Asian entrepreneurship, and the influx of Asian visitors have significantly contributed to Hawaii's economy.
The geographic proximity of Hawaii to Asia has facilitated travel, cultural exchange, and historical ties between Hawaii and Asian nations. The ease of travel and shared time zones have strengthened connections and fostered a mutual understanding.
Furthermore, Asians have made significant contributions to Hawaii's education system and professional workforce. Their academic achievements, representation in professional fields, and presence in educational institutions have positively influenced the quality of education and economic development in the islands.
In conclusion, the prevalence of Asians in Hawaii is a testament to their historical roots, cultural preservation, economic contributions, geographic proximity, and educational achievements. The Asian community's rich heritage and active participation in various aspects of Hawaiian society have shaped the multicultural fabric of the islands. Recognizing and appreciating the factors that have contributed to the significant presence of Asians in Hawaii enables us to embrace the diversity that defines the unique identity of the islands.












